- Deutsch
-
EnglishDeutschItaliaFrançais日本語한국의русскийSvenskaNederlandespañolPortuguêspolskiSuomiGaeilgeSlovenskáSlovenijaČeštinaMelayuMagyarországHrvatskaDanskromânescIndonesiaΕλλάδαБългарски езикAfrikaansIsiXhosaisiZululietuviųMaoriKongeriketМонголулсO'zbekTiếng ViệtहिंदीاردوKurdîCatalàBosnaEuskeraالعربيةفارسیCorsaChicheŵaעִבְרִיתLatviešuHausaБеларусьአማርኛRepublika e ShqipërisëEesti Vabariikíslenskaမြန်မာМакедонскиLëtzebuergeschსაქართველოCambodiaPilipinoAzərbaycanພາສາລາວবাংলা ভাষারپښتوmalaɡasʲКыргыз тилиAyitiҚазақшаSamoaසිංහලภาษาไทยУкраїнаKiswahiliCрпскиGalegoनेपालीSesothoТоҷикӣTürk diliગુજરાતીಕನ್ನಡkannaḍaमराठी
Dekodieren von USB-C-Pinschnittspezifikationen
- 2024/11/28
- 315
Katalog
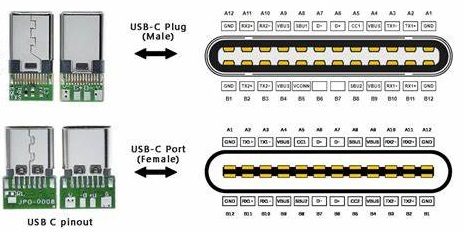
Überblick über USB-C-Pinout
USB-C bedeutet mehr als nur ein Steckerdesign.Es stellt ein Wahrzeichen der technologischen Kompatibilität dar.Als anfänglich mit USB4 kompatibeler Stecker unterstützt die Pin-Out-Struktur des USB-C eine flexible, reversible Steckerschnittstelle.Ein genauerer Blick auf den USB-Typ-C-Pinout zeigt die gespiegelte Konfiguration und zeigt deren Multifunktionalität.Jeder PIN spielt einzigartige Rollen: GND sorgt für die Erde;TX/RX-Paare ermöglichen die Hochgeschwindigkeitsdatenübertragung.VBUS Ergibt Strom, CC -PINs verwalten Konfigurationsaufgaben und SBU -Hilfsmittel bei der Verwendung von Seitenband.Diese Anpassungsfähigkeit zeigt sich in praktischen Anwendungen, in denen die USB-C-Fähigkeit, bestimmte Pins für zusätzliche Stromversorgung neu zuzuordnen, als vorteilhaft erweist.Diese Neuzuweisung hilft nicht nur bei der Unterstützung älterer Geräte, sondern verbessert auch die Geschwindigkeit und Effizienz für moderne Protokolle.
Die Vielseitigkeit von USB-C
Die Reversibilität des Designs ist eine hervorragende Funktion, die die Notwendigkeit einer Kabelorientierung beseitigt.Diese Bequemlichkeit spiegelt einen größeren Schritt in Richtung benutzerfreundlicher Technologie-Schnittstellen wider, in denen die Benutzerfreundlichkeit hervorgehoben wird.Darüber hinaus spiegelt die Kapazität des USB-C zur Einbeziehung unterschiedlicher Funktionen einen entstehenden Trend zum Zusammenführen mehrerer Technologien innerhalb eines einzelnen Standards wider.USB-C bezieht sich speziell auf das physikalische Anschlussdesign, getrennt von den von ihm unterstützten Datenübertragungsspezifikationen.Insbesondere ist es der erste Anschluss, der den neuesten USB4 -Standard unterstützen kann.Der Stecker -Pinout, der definiert, wie die Stecker- und Steckerschnittstelle reversibel ist, was bedeutet, dass die Verbindung in beide Richtungen hergestellt werden kann.Diese Flexibilität vereinfacht die Nutzung und verbessert die Haltbarkeit.Unten finden Sie eine Aufschlüsselung der USB-C-Pinout:
• GND (Masse): Rückflugebene für das Signal
• TX1+/TX2+: Positive Hochgeschwindigkeitsdifferenzdifferenzlinien
• TX1-/TX2-: Negative Hochgeschwindigkeitsdifferential-Paar-Linien
• vBUS: Stromversorgung
• CC1/CC2: Kanalkonfigurationsstifte
• D1+/D2+: Positive USB 2.0 -Differenzdatenlinien
• D1-/D2-: Negative USB 2.0-Differenzdatenlinien
• SBU1/SBU2: Seitenbandverwendung
• RX1+/RX2+: Positive Hochgeschwindigkeitsdifferenzdifferenzlinien
• RX1-/RX2-: Negative Hochgeschwindigkeitsdifferential-Paar-Linien
Dieses umfassende Pinout-Design ermöglicht es USB-C, nicht nur grundlegende USB-Operationen, sondern auch fortgeschrittenere Funktionen zu unterstützen, einschließlich Stromversorgung und Hochgeschwindigkeitsdatenübertragung.
Power- und Kompatibilitätsmodi in USB
Das Design von USB-C unterstützt mehrere Betriebsmodi mit erhöhter Funktionalität im Vergleich zu älteren USB-Standards.Es bleibt mit Legacy -Systemen wie USB 2.0 und USB 3.x kompatibel, wodurch es einfach ist, sich in eine Vielzahl von Umgebungen zu integrieren.Der Connector übernimmt über eine einzelne Schnittstelle Strom-, Daten- und Video-/Audio -Übertragung.
Dynamik des USB 2.0 -Modus
Der USB 2.0 -Modus verwendet ein einfaches Differentialpaar -Setup für die Übertragung von Daten.Aufgrund von Variationen der PIN-Konfigurationen tritt ein Adapter als Notwendigkeit auf, wenn USB-C mit USB 2.0 angeschlossen ist.Der achtsame Einsatz von Adaptern schützt vor elektrischen Fehlpaarungen, die verbundene Geräte hypothetisch schädigen könnten.Ein bemerkenswerter Aspekt von USB 2.0 liegt in seiner Unterstützung für verlängerte Kabellängen.Durch Ausschluss von Hochgeschwindigkeitsdatenlinien können Kabel bis zu vierfach die Länge der Standard-USB-C-Kabel erreichen.Dieses Merkmal wird in Situationen, in denen erhebliche Reichweite erforderlich ist, wie z. B. expansive Produktionsböden oder weit verbreitete Büroeinstellungen.Im Laufe der Zeit spricht die anhaltende Präsenz von USB 2.0 auf dem Markt für seine Belastbarkeit und Vielseitigkeit in zahlreichen technologischen Anwendungen.
Fortschritte im USB 3.x -Modus
Der USB 3.x-Modus bietet erhöhte Datenübertragungsraten über Hochgeschwindigkeitsdifferentialpaare und übertrifft seinen Vorgänger USB 2.0 erheblich.Die USB-C-Schnittstelle wurde neben USB 3.1 entwickelt und harmoniert mit allen USB-Standards ab 3.1, einschließlich USB4.Die Architektur unterstützt eine erhöhte aktuelle Lieferung und erhöht die Energieeffizienz, um eine Vielzahl von Geräteanforderungen zu erfüllen.Diese Kompatibilität betont die Anpassungsfähigkeit von USB-C in einem sich schnell verändernden technologischen Bereich und stellt eine nahtlose Mischung mit progressiven Innovationen sicher.Die Erfahrungen im Tech-Sektor zeigen seine Effektivität in Datenumgebungen mit hohen Bedingungen, wie z. B. Videoproduktion und Spielen, in denen die Reduzierung der Latenz eine Priorität hat.
Innovationen in der USB -Stromversorgung
Die USB -Leistungsdelieferung (PD) überträgt herkömmliche Einschränkungen und bietet bis zu 20 V/5A unter Verwendung einer geeigneten Verkabelung.Wenn ein Konfigurationskanal (CC) Pin vorhanden ist, ermöglicht er gleichzeitige Leistung und Datenfunktionen, die die Leistung der Geräte und die Ladeeffizienz verbessern.Diese doppelte Operationskapazität treibt Kreativität in der Geräteentwicklung an und unterstützt Flüssigkeitsfunktionen ohne Leistungsopfer.Getriebe Anwendungen wie in medizinischen Notfallwerkzeugen oder anspruchsvollen Computern zeigen, wie der PD -Modus in kritischen Situationen Zuverlässigkeit und Reaktivität aufrechterhalten.Die kontinuierliche Entwicklung der USB -Stromversorgung in diesen praktischen Szenarien beeinflusst die zukünftige Flugbahn und schafft ein neues Paradigma für Energielösungen in der Technologie.
Verbesserte Funktionen und Unterstützung für USB-C-Konnektivität
USB-C bietet mit dem alternativen Modus (ALT-Modus) eine noch größere Vielseitigkeit, sodass der Anschluss mehrere Daten- und Leistungsprotokolle unterstützen kann.Dies reduziert die Anzahl der erforderlichen Schnittstellen und vereinfacht die Gerätekonnektivität.
Vielseitige alternative Schnittstellen
USB-C, das für seinen vielfältigen alternativen Modus gefeiert wird, bietet die Möglichkeit, verschiedene Arten von Verbindungen über einen einzelnen Port zu erleichtern.Diese Funktion vereinfacht die komplexe Landschaft des elektronischen Designs mit hoher Dichte und ermöglicht schlanke, effiziente Konfigurationen, die die Leistung nicht beeinträchtigen.Die Kompatibilität mit Standards wie DisplayPort, MHL, Thunderbolt und HDMI bietet sanft die Notwendigkeit mehrerer zusätzlicher Ports beiseite, wodurch Design Agility und Verbesserung des Komforts unterstützt werden.Das Beherrschen der alternativen Modus hängt von einem Verständnis dieser Technologien ab, die häufig durch immersive Erfahrungen im Bereich des elektronischen Designs verfeinert werden.
Integrierte Audio -Lösungen
Der Audioadaptermodus von USB-C ist die Umgestaltung der Landschaft des Audiomanagements, indem es gleichzeitig das Aufladen neben der Audioausgabe ermöglicht.Diese einzigartige Fähigkeit nutzt ein USB 2.0 -Differentialpaar, wobei die Stern -Audio -Treue unabhängig davon, wie sich der Stecker orientiert, aufrechterhält.Durch das Weben von Ladefunktionen in Audiokonnektivität steigert sie die Erfahrung deutlich und vereinfacht den Prozess der Verknüpfung von Geräten.Die nahtlose Bewegung von traditionellen Audio-Buchsen bis USB-C löst einen natürlichen Fortschritt in Richtung integrierterer technologischer Lösungen ein.
Innovative Debugging -Fähigkeiten
Der Debug -Modus bietet unschätzbares Nutzen für Zubehörtests, indem CC -Pins so eingestellt wird, dass Differentialsignalpaare angepasst werden.Diese Funktionalität spielt eine große Rolle bei der Diagnose und Konfiguration von Geräten, da sie alle digitalen Schaltungsverbindungen vereinfacht, um sich auf eine präzise Signalanalyse zu konzentrieren.Während der Entwurfs- und Testphasen ist eine solche Präzision in Pin -Konfigurationen unabdingbar, um typische Konnektivitätsprobleme effektiv aufzulösen.Diese praktische Facette des USB-C-Designs erläutert das unerschütterliche Engagement der Branche für die Weiterentwicklung der Technologie für eine erhöhte Leistung.
Abschluss
Die Fähigkeit von USB-C, eine breite Palette von Protokollen, Stromversorgung und Hochgeschwindigkeitsdatenübertragung über einen einzelnen, kompakten Anschluss zu unterstützen, unterscheidet sie voneinander.Das Verständnis der USB-C-Pinout ist für die Gestaltung funktionaler, zukunftssicherer Geräte von wesentlicher Bedeutung.Mit seiner Rückwärtskompatibilität und Unterstützung für moderne Daten- und Leistungsanforderungen ist USB-C die optimale Wahl, um die Konnektivität über verschiedene Anwendungen hinweg zu vereinfachen.Durch die Verwendung der vollständigen Funktionen von USB-C können Sie die Komplexität reduzieren, Designs rationalisieren und die Geräteleistung verbessern.
Verwandter Blog
-
Netzteilspannung Abkürzung: VCC VDD VEE VSS GND

2024/06/6
Im modernen elektronischen Schaltungsdesign, Verständnis der Abkürzungen der Stromversorgungsspannung (wie VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, GND).Diese Abkürzung... -
Ein Überblick über TTL- und CMOS -ICs und wie Sie zwischen ihnen wählen

2024/04/13
In diesem Artikel werfen wir einen detaillierten Blick auf zwei wichtige elektronische Technologien, komplementäre Metaloxid-Halbleiter (CMOS) und Tr... -
Verschiedene Arten von Sicherungen und Anwendungen

2024/04/18
Sicherungen sind wesentliche Komponenten in modernen elektrischen Systemen und fungieren als entscheidende Beschützer vor Überstrom.Sie arbeiten, in... -
Verständnis des C1815 -Transistors: Pinouts, Schaltungssymbole, Anwendungsschaltungen

2023/12/20
Welche Art von Röhre ist der C1815?C1815 Triode PinoutC1815 ModellzeichnungC1815 -ParameterC1815 EigenschaftenAnwendung von C1815 Der C1815 -Transist... -
LR44 -Batterien: LR44 -Batterieäquivalente und LR44 -Batterieersatz

2024/01/24
In einem sich schnell entwickelnden technologischen Gebiet, in dem die Größe der elektronischen Geräte weiter schrumpfen und dennoch alltäglicher ... -
Grundkenntnisse über Sicherungen: Merkmale, Arbeitsprinzipien, Typen und wie man richtig auswählt

2024/04/10
Sicherungen schützen Schaltungen vor Schäden aufgrund von Überlastung oder Kurzstrecken.Dieses einfache, aber geniale Gerät basiert auf einem leic... -
Leitfaden zu Buck-, Boost- und Buck-Boost-Konverter

2023/12/21
Was ist ein Buck -Konverter?Wie funktioniert ein Buck Converter?Was ist ein Boost -Konverter?Wie funktioniert ein Boost -Konverter?Was ist ein Auftrie... -
Gesamtzahl der Transistoren in einer CPU
2024/06/14
In der modernen Computertechnologie ist die Beziehung zwischen der zentralen Verarbeitungseinheit (CPU) und den Transistoren zunehmend integraler gewo... -
Grunde elektronische Grundkomponenten verstehen - Widerstände, Kondensatoren, Dioden, Transistoren, Induktoren und digitale Logik -Tore

2024/04/13
Elektronische Komponenten sind der Eckpfeiler des Bauens und der Optimierung elektronischer Schaltkreise.Von gewöhnlichen Haushaltsgeräten bis hin z... -
Beschreiben Sie kurz die Spezifikationen, Verpackungen, das Arbeitsprinzip, die Vorteile und die Umweltauswirkungen von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien

2024/03/20
Seit der Einführung von wiederaufladbaren Blei-Säure-Batterien im Jahr 1859 wurden sie allmählich in den Gewebe des technologischen Fortschritts ei... -
Beherrschen analoge und digitale Schaltungen: Ein Anfängerführer

2023/12/20
Definition und Eigenschaften von analogen Schaltungen und digitalen SchaltungenDer Unterschied zwischen analogen Schaltungen und digitalen Schaltungen... -
Transistor (BJT und MOSFET) Arbeitsprinzipien

2023/12/20
Arbeitsprinzip des bipolaren Junction -Transistors (BJT)Auswahl der KomponentenwerteWie wählen Sie einen Transistor?Arbeitsprinzip von MOSFETWie scha... -
Eine vollständige Liste von Testmethoden für verschiedene Transistoren

2023/12/20
Der Transistor wurde von John Bardeen, William Shockley und Walter Brattain erfunden.Es handelt sich um ein Kollektor-, Emitter- und Basis-Drei-termin...
Heiße Teile
- GCM1555C1HR50CA16D
- 12061C103K4T4A
- GCM2165C2A391JA16D
- 08051A220FAT4A
- 08051U121GAT2A
- 12065A300DAT2A
- 1808GC150MAT1A
- 22205C106M4Z2A
- GRM1555C1E9R9CZ01D
- GRM1556S1H330JZ01D
- T491A684K020AT
- MPC940LACR2
- SRF0905-400Y
- EPF10K10ATC100-2
- TLV376IDR
- TWL6032A1B6YFFR
- ISL6843IUZ
- MCP2200-I/SS
- MAX1480ACPI
- RT1206BRE071K6L
- LPS25HBTR
- DSPIC33EP512MU814-I/PL
- AD8542ARZ
- RC0805FR-0710K2L
- SC508ULTRT
- V300B2V2C100B
- PT8914-S
- EP104PBF
- XC2S100E-7PQG208C
- HD6473308F10
- LA7356ML-TRM
- AM29F200BT-55EC
- LM4867MTEX
- F931C686MCCAJ6
- EP224LC-10A
- MB86277PMC-G-BNDE1
- UPD65958N7T03
- M30622MGP-223FP
- MAP5401M-QB-E5-060
- EN29LV800AB
- UCC5672WP
- DP83TC811SWRNDTQ1
- PMB6848.E100
- M38B79MFH-A076FP
- ICS844021BGI-01LF
- SN74LS06NSE4
- HMC346MS8G(E)
- HG-KR23


