- Deutsch
-
EnglishDeutschItaliaFrançais日本語한국의русскийSvenskaNederlandespañolPortuguêspolskiSuomiGaeilgeSlovenskáSlovenijaČeštinaMelayuMagyarországHrvatskaDanskromânescIndonesiaΕλλάδαБългарски езикAfrikaansIsiXhosaisiZululietuviųMaoriKongeriketМонголулсO'zbekTiếng ViệtहिंदीاردوKurdîCatalàBosnaEuskeraالعربيةفارسیCorsaChicheŵaעִבְרִיתLatviešuHausaБеларусьአማርኛRepublika e ShqipërisëEesti Vabariikíslenskaမြန်မာМакедонскиLëtzebuergeschსაქართველოCambodiaPilipinoAzərbaycanພາສາລາວবাংলা ভাষারپښتوmalaɡasʲКыргыз тилиAyitiҚазақшаSamoaසිංහලภาษาไทยУкраїнаKiswahiliCрпскиGalegoनेपालीSesothoТоҷикӣTürk diliગુજરાતીಕನ್ನಡkannaḍaमराठी
Umfassender Leitfaden zum Laden einer Autobatterie
- 2024/10/25
- 309
Katalog
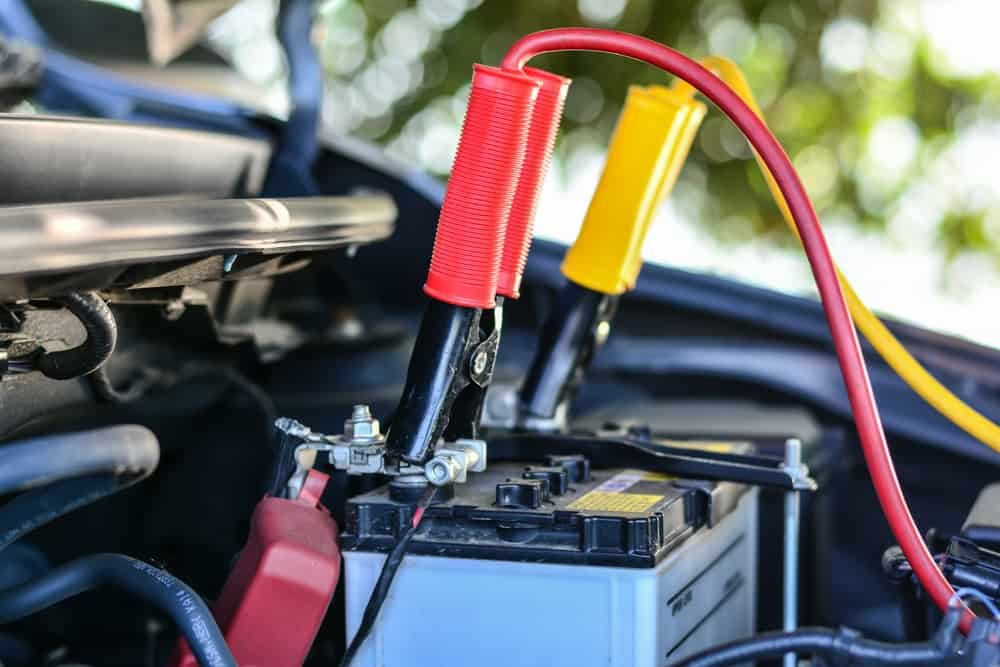

Effiziente Ladung für Automaten
In der Regel das Laden einer 12-Volt-Auto-Batterie mit einem Standard-Ladegerät.Abhängig vom Zustand des Akkus und des verwendeten Ladegeräts kann es jedoch länger dauern.Wenn die Batterie erschöpft ist, kann es 10 bis 24 Stunden benötigen, um die volle Kapazität zu erreichen.Das regelmäßige Aufladen Ihrer Batterie ist besonders wichtig, wenn Ihr Auto mehrere Tage lang im Leerlauf sitzt, da parasitäre Unentschieden aus der Elektronik Ihres Fahrzeugs schnell die Stromversorgung abnehmen können.
Schritte zum Laden einer Autobatterie
Stellen Sie vor dem Start sicher, dass Sie sich in einem gut belüfteten Bereich befinden, vorzugsweise im Freien oder in einer Garage mit ordnungsgemäßem Luftstrom.Hier sind die wesentlichen Schritte, die Sie befolgen sollten:
- Sicherheit zuerst: Entfernen Sie Schmuck, Tragen Sie Handschuhe und Sicherheitsbrillen und verbinden Sie eine Backup-Batterie mit dem OBD-II-Anschluss, um die Elektronik Ihres Autos während des Ladevorgangs zu schützen.
- Die negative Klemme trennen: Beginnen Sie zunächst, das negative Klemmen (normalerweise schwarz) zu trennen, um elektrische Kurzfilme zu verhindern.Verwenden Sie einen Lappen oder Handschuh, um das Terminal abzudecken.
- Verbinden Sie das Ladegerät: Schließen Sie die positive Klemme des Ladegeräts mit dem positiven Klemme der Batterie und der negativen Klemme an den negativen Anschluss an.Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie das positive Terminal mit der negativen Klemme des Ladegeräts nicht berühren.
- Stecker das Ladegerät: Fügen Sie das Ladegerät in eine Steckdose ein und überprüfen Sie die Einstellungen entsprechend dem Batteriestyp und der Spannung.
- Setzen Sie das Ladegerät: Passen Sie die Ladeeinstellungen auf 12 Volt an und wählen Sie gegebenenfalls „überflutet“ oder „nass“ aus.Die meisten intelligenten Ladegeräte erkennen automatisch den Akku -Typ.
- Lade anfangen: Schalten Sie das Ladegerät ein und überwachen Sie den Ladevorgang.Erwarten Sie abhängig vom Ladegerät 4 bis 8 Stunden für Teilgebühren und 10 bis 24 Stunden für eine vollständige Ladung.
- Trennen Sie die Verbindung, wenn Sie fertig sind: Sobald das Laden abgeschlossen ist, sollte der Akku ungefähr 12,88 Volt lesen.Trennen Sie das Ladegerät und stellen Sie sicher, dass sich die Klemmen weder einander noch die Klemmen berühren.
- Verbinden Sie den negativen Terminal wieder: Schließlich verbinden Sie das negative Anschluss wieder mit der Batterie und trennen Sie jede Sicherungsquelle, die Sie möglicherweise verwendet haben.
Auswahl des richtigen Batterieladegeräts
Durch die Auswahl des entsprechenden Ladegeräts kann die Ladeeffizienz und die Gesundheit der Batterie verlängert werden.Das Verständnis der verschiedenen verfügbaren Arten von Ladegeräten ist insbesondere für die Aufrechterhaltung einer hohen Leistungsleistung in der Batterie Ihres Fahrzeugs erforderlich.
Smart Battery Ladegeräte
Diese Ladegeräte enthalten fortschrittliche Technologie, mit der sie die Spannung und Stromstärke der Batterie während des gesamten Ladevorgangs kontinuierlich überwachen können..Diese Fähigkeit hilft, den Ladevorgang zu optimieren und die Batterie vor Überladen zu schützen, was zu einer Schädigung oder einer verringerten Lebensdauer führen kann.Darüber hinaus bieten viele intelligente Ladegeräte mehrere Lademodi an, wie "Bulk", "Absorption" und "Float", um sicherzustellen, dass die Batterie in jeder Phase sicher und effizient geladen wird.Sie sind auch mit integrierten Sicherheitsmerkmalen ausgestattet, einschließlich Schutz vor kurzer Kreislauf, umgekehrter Polarität und Überhitzung, wodurch sie sicherer zu bedienen sind.Smart-Battery-Ladegeräte sind ideal für den regelmäßigen Gebrauch, insbesondere für diejenigen, die aufgrund von kurzen Reisen oder Abhängigkeiten auf elektrisches Zubehör häufig Batterie-Abfluss erleben, da sie ein zuverlässiges und problemloses Ladeerlebnis bieten.
Trickle Ladegeräte
Diese Ladegeräte sind so konzipiert, dass sie einen langsamen, stetigen Stromfluss liefern und sie für Fahrzeuge geeignet sind, die nicht regelmäßig angetrieben werden.Sie sind vorteilhaft, da sie die Ladung der Batterie beibehalten, ohne sie zu überwältigen, und so eine Sulfatierung verhindern, was ein häufiges Problem bei Blei-Säure-Batterien ist, die zu einem Kapazitätsverlust führen können.Trickle-Ladegeräte bieten Vielseitigkeit, wobei viele sowohl in Plug-in- als auch in solarbetriebenen Versionen erhältlich sind, sodass Sie basierend auf ihrer Umgebung und ihren Bedürfnissen auswählen können.Die meisten Trickladegeräte verfügen außerdem über automatische Absperrung und stoppen den Ladevorgang, sobald die Batterie voll ist, um eine Überladen zu verhindern.Diese Ladegeräte eignen sich gut für Klassiker, Motorräder oder Freizeitfahrzeuge (Wohnmobile), die über längere Zeiträume stationär bleiben, und sie sind für saisonale Fahrzeuge wirksam, die gelegentlich Wartungsgebühren erfordern.
Batterieverwalter
Es wird häufig als Batteriewerke bezeichnet, so konstruiert, dass eine Batterie auf einer konsistenten Spannung aufbewahrt wird, anstatt sie vollständig aufzuladen.Sie bewahren die Gesundheit von Batterien, die für lange Dauern untätig bleiben.Die Batterieversehler überwachen die Spannung der Batterie kontinuierlich und bieten ein kleines Stromrinkel, um den gewünschten Ladungsniveau aufrechtzuerhalten, was die Selbstentscheidung effektiv verhindert.Viele moderne Betreuer nutzen die Mikroprozessor -Technologie, um intelligent zu bestimmen, wann Strom versorgt werden soll, und stellen Sie sicher, dass die Batterie ohne Überlastung abgeschaltet bleibt.Batterieverwalter sind für Fahrzeuge von Vorteil, die für lange Zeiträume selten eingesetzt oder gelagert werden, z. B. Boote, Oldtimer und Motorräder.Sie sind erforderlich, um Tiefzyklus-Batterien in gutem Zustand zu halten, insbesondere in saisonalen Anwendungen.
Verständnis der Autobatteriespannung
Eine voll aufgeladene Auto -Batterie sollte ungefähr 12,88 Volt messen.Elektrische Systeme für Automobile arbeiten mit 12 Volt, und es gibt nur einen 1,04-Volt-Unterschied zwischen einer voll aufgeladenen und einer völlig toten Batterie.Bemerkenswerterweise kann eine Batterie, die nur 0,2 Volt unter vollen Ladung liegt, deuten darauf hin, dass ein dauerhafter Fehler ist.Beispielsweise zeigt eine Messung von 12,68 Volt auf eine schwache Batterie, die das Aufladen erfordert.
Wenn Sie ein Multimeter verwenden, um die Spannung Ihres Akkus zu überprüfen, finden Sie hier ein kurzes Referenzdiagramm für die Interpretation der Messwerte:
|
Zustand
der Ladung |
Stromspannung |
|
100% |
12.88 |
|
75% |
12.64 |
|
50% |
12.39 |
|
25% |
12.09 |
|
0% |
11.80 |
Um die Akkulaufzeit zu verlängern, ist es erforderlich, eine Ladung zwischen 90% und 100% konsistent zu halten.Wenn dies nicht der Fall ist, kann dies zu einem vorzeitigen Verschlechterung und einem eventuellen Ausfall der Batterie führen.
Timing -Tipps für Autobatterien aufladen
Zu wissen, wann Sie Ihre Automobilbatterie aufladen müssen, ist insbesondere für die Aufrechterhaltung der Fahrzeugleistung und die Vermeidung unerwarteter Zusammenhänge wichtig.Autobatterien können aufgrund verschiedener Faktoren, einschließlich Alter, Wetterbedingungen und der Häufigkeit des Fahrzeuggebrauchs, die Ladung verlieren.Das Erkennen der Anzeichen einer schwachen Batterie und das Verständnis, wie oft das Aufladen zu sein, kann dazu beitragen, die Lebensdauer zu verlängern und sicherzustellen, dass Ihr Fahrzeug zuverlässig bleibt.In diesem Leitfaden untersuchen wir Indikatoren, die die Notwendigkeit einer Aufladung signalisieren, und bieten Tipps zur ordnungsgemäßen Batteriewartung
Erwägen Sie, Ihre Batterie in den folgenden Situationen aufzuladen:
- Nach dem Springen Ihres Fahrzeugs
- Wenn Sie ein ungewöhnliches Verhalten in Ihrem elektrischen Zubehör bemerken
- Wenn Sie ein inneres Licht angelassen haben
- Wenn Ihr Auto träge startet
- Wenn Sie während der Zündung ungewöhnliche Geräusche hören
- Regelmäßiges Aufladen kann tiefe Entladungen verhindern, die zu einer dauerhaften Batterieschäden führen können.
Aufladen einer toten Autokatterie
Das Aufladen einer völlig toten Batterie kann eine Herausforderung sein.Vollmachte Batterien erfordern möglicherweise mehr Zeit.Wenn eine Batterie jedoch über einen längeren Zeitraum tot ist, kann dies aufgrund eines als Sulfatierung bekannten Verfahrens, der dauerhafte Schäden verursachen kann, möglicherweise nicht vollständig aufgeladen.Es gleicht eine effiziente Energieübertragung durch Batteriepflege aus.Untersuchungen deuten darauf hin, dass die Aufrechterhaltung der Stabilität bei der Ladevorgänge unerwartete Fahrzeugprobleme in der Tat mildern kann.
Ladevorgang erklärt
Um dies zu vermeiden, sind die Ladegeräte für die Autobatterie so ausgelegt, dass sie langsam und stetig aufladen.Ladegeräte arbeiten in der Regel mit Spannungen von 13 bis 14 Volt, was erforderlich ist, um den Strom in die Batterie zu drücken.Stellen Sie sich die Spannung als elektrischen Druck vor, wie es bei der Aufblendung des Luftes in einen Ballon schwieriger wird, und das Aufladen einer Batterie erfordert eine Erhöhung der Spannung, um sie mit Strom zu füllen.Die Ladegeräte müssen jedoch darauf achten, 16 Volt nicht zu überschreiten, da dies die empfindliche Elektronik eines Autos beschädigen könnte.Smart Ladegeräte regulieren die Spannung automatisch, um eine Überhitzung zu verhindern. Dabei dauern jedoch länger, um die Ladung abzuschließen.
Das Laden erfolgt in drei Phasen:
- Schüttungsphase: Diese Phase lädt den Akku relativ schnell auf etwa 75% Kapazität auf, da er nicht viel von einer Spannungserhöhung erfordert.Obwohl es schnell ist, wird es kontrolliert, um eine Überhitzung zu verhindern.Auch bei 75%ist die Batterie nicht vollständig bereit, ein Fahrzeug lange mit Strom zu versorgen.
- Absorptionsphase: Sobald die Batterie zu 75% aufgeladen ist, muss das Ladegerät die Spannung erhöhen, um mehr Energie hineinzudrängen.Diese Phase ist langsamer, da höhere Spannungen das Risiko einer mehr Wärme erzeugen, und das Ladegerät arbeitet sorgfältig zusammen, um zu verhindern, dass die Batterie überhitzt.Es kann noch einige Stunden dauern, bis die volle Ladung erreicht ist.
- Schwimmerphase: Nachdem die Batterie die volle Ladung erreicht hat, behält das Ladegerät es bei 100% bei, indem sie gerade genug Energie liefert, um natürliche Entladung auszugleichen.Diese Phase verwandelt das Ladegerät effektiv in ein Trickle -Ladegerät, um sicherzustellen, dass die Batterie ohne Überhitzung abgeschaltet bleibt.
Die Ladezeit wird verlängert, um die Batterie vor übermäßiger Hitze zu schützen, und es ist wichtig, den Prozess nicht zu beschleunigen.Das Aufladen in einer kühleren Umgebung kann dazu beitragen, die Lebensdauer der Batterie zu verlängern.Das Entfernen der Batterie aus dem Ladegerät, bevor sie vollständig aufgeladen ist, kann zu unvollständigem Laden führen, was zu einer schwachen Batterie führt, die das Auto nicht zuverlässig startet.
Sie können eine tote Autokatterie nicht vollständig aufladen
Eine vollständig tote Autokatterie kann nicht vollständig aufgeladen werden.Wenn eine Batterie 0% Ladung erreicht, litt sie aufgrund eines als Sulfatierung bekannten Verfahrens an irreversiblen Schäden.Die Sulfatierung tritt auf, wenn Bleisulfatkristalle bilden und die Innenplatten der Batterie härten, was verhindert, dass sie eine Ladung halten.Wenn Sie früh gefangen werden, kann ein Teil der Schäden durch die Sulfatierung mit dem richtigen Ladegerät umgekehrt werden.In vielen Fällen wird eine sulfizierte Batterie jedoch niemals auf ihre ursprüngliche Kapazität aufgeladen.Beispielsweise kann eine zu 50% berechnete Batterie möglicherweise nur nach dem Gebühren eine Kapazität von 50% erreichen, unabhängig davon, wie lange es auf dem Ladegerät dauert.In solchen Fällen ist es normalerweise besser, die alte Batterie zu recyceln und durch ein neues zu ersetzen, um weitere Probleme zu vermeiden, z.
Zeit erforderlich, um eine Autobatterie durch das Fahren aufzuladen
Wenn Sie sich auf das Fahren verlassen, um Ihre Autobatterie wieder aufzuladen 4 bis 8 Stunden Autobahn fahren.Dies liegt daran, dass die Lichtmaschine, obwohl sie für die Aufrechterhaltung der Batterieladung während des Betriebs verantwortlich ist, hauptsächlich mit der Einführung der Elektronik des Fahrzeugs wie Lichtern, Armaturenbrettanzeigen und Motorsteuereinheiten verantwortlich ist.
Damit die Lichtmaschine mit dem Aufladen des Akkus beginnen kann, muss der Motor mit der oben genannten Geschwindigkeit laufen 1.000 U / minund selbst dann ist die Ladungsrate relativ langsam.Während eine kurze 30 Minuten Das Laufwerk kann der Batterie einen kleinen Schub verleihen. Er reicht nicht aus, um einen abgereicherten Akku vollständig aufzuladen.Wenn Ihre Batterie niedrig ist, ist es viel effizienter, ein dediziertes Ladegerät zu verwenden, anstatt sich auf Ihre Lichtmaschine zu verlassen, da das Fahren allein einen tief entladenen Akku nicht ausreichend auflädt.
Jumper -Kabel können eine Automobilbatterie nicht aufladen und aufladen
Sprungstarter sind nicht so ausgelegt, dass sie eine Autokatterie aufladen.Stattdessen ist es ihr Ziel, dem Starter des Autos einen schnellen Strom zu gewährleisten, sodass der Motor beginnen kann.Jump-Starter liefern einen temporären Schub (typischerweise etwa 12 Ampere bei 14-15 Volt), was weitaus geringer ist als eine voll geladene Auto-Batterie.Eine typische Autokatterie ist in der Lage, Hunderte von Cold -Cranking -Verstärkern (CCA) zu liefern, die zum Umdrehen des Motors benötigt werden.
Nach dem Sprungstart beginnt die Lichtmaschine des Fahrzeugs, die Batterie aufzuladen, aber es ist keine ideale Methode für eine vollständige Aufladung.Um einen abgelassenen Akku ordnungsgemäß aufzuladen, müssten Sie mehrere Stunden lang mit Autobahngeschwindigkeiten fahren, was keine praktische Lösung darstellt.Stattdessen ist die Verwendung eines dedizierten Auto -Batterie -Ladegeräts eine effektivere Möglichkeit, die Ladung einer Batterie wiederherzustellen.Das Laden einer Autobatterie mit Pulloverkabel ist unwirksam und wird im Wesentlichen viel zu lange dauern.Jumper -Kabel sind so konzipiert, dass sie Strom von einem Lauffahrzeug direkt auf den Starter eines toten Autos übertragen, wobei die Batterie umgeht.Nach dem Start des toten Autos hilft das, die angeschlossenen Kabel, die tote Batterie nicht wieder aufzuladen.
Darüber hinaus hilft die Wiederbelebung des Motors des Autos, der den Sprung sorgt, auch nicht, die tote Batterie zu berechnen.Stattdessen verteilt die Lichtmaschine des Laufwagens einfach die zusätzliche Leistung an seine eigene Elektronik.Der Versuch, eine tote Batterie über Pulloverkabel zu laden, kann auch die Schäden der elektrischen Systeme beider Autos riskieren.Verwenden Sie immer ein dediziertes Batterieladegerät, nicht um Pulloverkabel, um eine Auto -Batterie sicher und effektiv aufzuladen.
Erkennen und Vermeidung einer Überladung einer Autobatterie
Das Überladen einer Autobatterie kann zu Beschädigungen führen. Es ist erforderlich, die Schilder frühzeitig zu erkennen.Häufige Symptome einer Überladung sind:
- Der Geruch von faulen Eiern: Dies ist darauf zurückzuführen, dass Schwefelgase aus der Batterie entkommen.
- Zischend klingt: Eine Batterie, die ein zischendes Geräusch herstellt, freisetzt Gas aufgrund von Überhitzung.
- Übermäßige Hitze: Wenn sich das Batteriegehäuse heiß anfühlt, ist es eine Überhitzung.
Überladen tritt auf, wenn die Batterie zu heiß wird, wodurch Wasser innerhalb der Batterie verdampft.Dies kann zu internen Schäden führen und die Lebensdauer der Batterie verringern.Um Überladen zu vermeiden, stellen Sie immer sicher, dass die Ladeeinstellungen Ihrem Akku übereinstimmen.
Verwandter Blog
-
Netzteilspannung Abkürzung: VCC VDD VEE VSS GND

2024/06/6
Im modernen elektronischen Schaltungsdesign, Verständnis der Abkürzungen der Stromversorgungsspannung (wie VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, GND).Diese Abkürzung... -
Ein Überblick über TTL- und CMOS -ICs und wie Sie zwischen ihnen wählen

2024/04/13
In diesem Artikel werfen wir einen detaillierten Blick auf zwei wichtige elektronische Technologien, komplementäre Metaloxid-Halbleiter (CMOS) und Tr... -
Verschiedene Arten von Sicherungen und Anwendungen

2024/04/18
Sicherungen sind wesentliche Komponenten in modernen elektrischen Systemen und fungieren als entscheidende Beschützer vor Überstrom.Sie arbeiten, in... -
Verständnis des C1815 -Transistors: Pinouts, Schaltungssymbole, Anwendungsschaltungen

2023/12/20
Welche Art von Röhre ist der C1815?C1815 Triode PinoutC1815 ModellzeichnungC1815 -ParameterC1815 EigenschaftenAnwendung von C1815 Der C1815 -Transist... -
LR44 -Batterien: LR44 -Batterieäquivalente und LR44 -Batterieersatz

2024/01/24
In einem sich schnell entwickelnden technologischen Gebiet, in dem die Größe der elektronischen Geräte weiter schrumpfen und dennoch alltäglicher ... -
Leitfaden zu Buck-, Boost- und Buck-Boost-Konverter

2023/12/21
Was ist ein Buck -Konverter?Wie funktioniert ein Buck Converter?Was ist ein Boost -Konverter?Wie funktioniert ein Boost -Konverter?Was ist ein Auftrie... -
Grundkenntnisse über Sicherungen: Merkmale, Arbeitsprinzipien, Typen und wie man richtig auswählt

2024/04/10
Sicherungen schützen Schaltungen vor Schäden aufgrund von Überlastung oder Kurzstrecken.Dieses einfache, aber geniale Gerät basiert auf einem leic... -
Gesamtzahl der Transistoren in einer CPU
2024/06/14
In der modernen Computertechnologie ist die Beziehung zwischen der zentralen Verarbeitungseinheit (CPU) und den Transistoren zunehmend integraler gewo... -
Grunde elektronische Grundkomponenten verstehen - Widerstände, Kondensatoren, Dioden, Transistoren, Induktoren und digitale Logik -Tore

2024/04/13
Elektronische Komponenten sind der Eckpfeiler des Bauens und der Optimierung elektronischer Schaltkreise.Von gewöhnlichen Haushaltsgeräten bis hin z... -
Beschreiben Sie kurz die Spezifikationen, Verpackungen, das Arbeitsprinzip, die Vorteile und die Umweltauswirkungen von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien

2024/03/20
Seit der Einführung von wiederaufladbaren Blei-Säure-Batterien im Jahr 1859 wurden sie allmählich in den Gewebe des technologischen Fortschritts ei... -
Beherrschen analoge und digitale Schaltungen: Ein Anfängerführer

2023/12/20
Definition und Eigenschaften von analogen Schaltungen und digitalen SchaltungenDer Unterschied zwischen analogen Schaltungen und digitalen Schaltungen... -
Wie viele Spannungen sollte eine Autokatterie haben?

2024/08/25
Ist es wirklich genug zu sagen, dass eine Batterie bei 11,9 Volt oder höher "vollständig aufgeladen" ist?Diese Zahl bietet eindeutig eine Grundlinie... -
Transistor (BJT und MOSFET) Arbeitsprinzipien

2023/12/20
Arbeitsprinzip des bipolaren Junction -Transistors (BJT)Auswahl der KomponentenwerteWie wählen Sie einen Transistor?Arbeitsprinzip von MOSFETWie scha...
Heiße Teile
- C1005C0G1H560J050BA
- CGA3E2C0G1H121J080AD
- 12062A821KAT2A
- GQM1555C2D4R6WB01D
- 12105U102JAT2A
- GCM1555C1H2R2CZ13D
- TPSC157K006R0090
- 165034
- BAT54A
- MCC44-12IO1B
- XC4VLX25-11FFG668C
- MAX4518CSD+T
- ISO7631FCDW
- Z85C3008PEC
- SN74LS123NSR
- LMH2832IRHAT
- AH373-WG-7
- 2MBI400NB-060-01
- CM75BU-24NFM
- ER1002FCT
- LT1365CS
- X28HC256S-12
- BS616LV8016FCP70
- 2SK3264
- AM29205-16KC
- S5L9290X02
- AD7008AP20
- RT1P431M-T111-1
- HY62256-70LL
- W27C512-45
- LD7550IL
- MAX1928EUB15
- TMP87C405M-1H29
- STP2200ABGA
- SI3201-X-FS
- GMS34140-RA079
- M58CR032C100ZB6T
- M74HC4511M1R
- SC1485ITS.TRT
- MAX733CWE
- PPC440EP-3BC400C
- SC26C198C1A
- AD8221BRZ-REEL7
- S29GL032A90FAIR30
- SB-5504-ML-TR
- STDP9310-BB
- MT7615DN
- MTFC4GMDEA-4M


