Alle Kategorien
-
Integrierte schaltkreise (ICS)
Integrierte schaltkreise (ICS)
- Schnittstelle - Sensor, kapazitive Berührung(642)
- Spezialisierte ICS(12188)
- PMIC-Spannungsregler-besonderer Zweck(5644)
- PMIC-Spannungsregler-lineare Regler(793)
- PMIC-Spannungsregler-linear + Switching(1829)
- PMIC-Spannungsregler-linear(70981)
- PMIC-Spannungsregler-DC DC Switching Regulators(39569)
- PMIC-Regler-DC-DC-Switching-Controller(13507)
- PMIC-Spannungs-Referenz(9453)
- PMIC-v/f und f/v-Wandler(145)
- PMIC-Thermal Management(592)
- PMIC-Supervisor(47946)
- PMIC-RMS bis DC-Wandler(170)
- PMIC-Netzteil-Controller, Monitore(2104)
- PMIC-Power over Ethernet (PoE) Controller(1008)
- PMIC-Power Management-spezialisierte(7722)
- PMIC-Netzschalter, Treiber laden(7706)
- PMIC-PFC (Power Factor Correction)(1222)
- PMIC oder Steuerungen, ideale Dioden(705)
- PMIC-Motor-Treiber, Regler(4712)
- PMIC-Beleuchtung, Ballast-Regler(560)
- PMIC-LED-Treiber(7282)
- PMIC-Laser-Treiber(573)
- PMIC-Hot-Swap-Controller(2816)
- PMIC-Gate-Treiber(7083)
- PMIC-voll, Half-Bridge-Treiber(1342)
- PMIC-Energy Messung(654)
- PMIC-Display-Treiber(1435)
- PMIC-derzeitige Regulierung/Management(1481)
- PMIC-Batterie-Management(5553)
- PMIC-Ladegeräte(3831)
- PMIC-AC DC Konverter, Offline Schalter(4905)
- Memory-Controller(358)
- Memory-Konfigurations-Proms für FPGAs(639)
- Speicher-Akkus(13)
- Erinnerung(65446)
- Logic-universelle Bus-Funktionen(706)
- Logic-Übersetzer, Level-Shifter(2854)
- Logik-Specialty Logic(1870)
- Logik-Signal-Schalter, Multiplexer, Decoder(9420)
- Logic-Shift-Register(2665)
- Logic-Parity Generatoren und Checkers(335)
- Logic-multivibratoren(831)
- Logik-Latches(3658)
- Logik - Tore und Wechselrichter - Multifunktion, konfigurierbar(1687)
- Logik-Tore und Wechselrichter(16453)
- Logic-Flip Flops(7780)
- Logik-FIFOs Speicher(4240)
- Logik-Zähler, Trennlinien(3456)
- Logik-Vergleichsoperator(592)
- Logik-Puffer, Treiber, Receiver, Transceiver(17835)
- Linear-Video-Verarbeitung(2909)
- Linear-Vergleichsoperator(5084)
- Linear-analoge Multiplikatoren, Trennwände(263)
- Linear-Verstärker-Video Amps und Module(1905)
- Linear-Verstärker-Spezial-Zweck(1856)
- Linear - Verstärker - Instrumentierung, OP -Verstärker, Pufferverstärker(34236)
- Linear-Verstärker-Audio(4567)
- Interface-Voice Record und Playback(556)
- Schnittstelle - UARTs (Universal Asynchronous Receivers -Sender)(1236)
- Schnittstelle-Telecom(4467)
- Interface-spezialisierte(4833)
- Interface-Signal Terminatoren(333)
- Interface-Signal-Puffer, Repeater, Splitter(1449)
- Interface-Serializer, Deserializer(1480)
- Schnittstellen-Sensor und Detektor-Interfaces(1524)
- Interface-Module(169)
- Interface-Modems-ICS und Module(407)
- Interface-e/a-Expander(1136)
- Interface-Filter-aktiv(1226)
- Interface-Encoder, Decoder, Konverter(714)
- Interface-Treiber, Receiver, Transceiver(20755)
- Interface-Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)(117)
- Interface-Controller(3628)
- Interface-Codecs(1676)
- Schnittstelle - Analoge Switches, Multiplexer, Demultiplexer(12567)
- Schnittstelle-analoge Schalter-spezieller Zweck(2533)
- Embedded-System on Chip (SoC)(4496)
- Embedded-PLDs (programmierbare Logik-Vorrichtung)(971)
- Embedded-Mikroprozessoren(10083)
- Embedded-Mikrocontroller-anwendungsspezifische(2275)
- Embedded-Mikrocontroller(99285)
- Eingebettet - Mikrocontroller, Mikroprozessor, FPGA -Module(1527)
- Eingebettet - FPGAs (Feldprogrammiergate -Array) mit Mikrocontrollern(81)
- Embedded-FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)(27748)
- Embedded-DSP (Digital Signal Processors)(4081)
- Eingebettet - CPLDs (komplexe programmierbare Logikgeräte)(5187)
- Datenerfassung-Touch Screen Controller(1210)
- Datenerfassung-Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)(14419)
- Datenerfassung-digitale Potentiometer(6250)
- Datenerfassung-analog zu Digital Converters (ADC)(17776)
- Datenerfassung-analoges Frontend (AFE)(787)
- Datenerfassung-MDE/DACs-spezieller Zweck(3043)
- Clock/Timing-Uhren in Echtzeit(2446)
- Uhr/Timing - programmierbare Timer und Oszillatoren(23469)
- Clock/Timing-IC-Akkus(4)
- Takt/Timing-Delay Lines(1049)
- Uhr/Timing - Uhrengeneratoren, PLLS, Frequenzsynthesizer(32775)
- Clock/Timing-Clock Puffer, Treiber(4568)
- Clock/Timing-anwendungsspezifische(8652)
- Audio Spezial-Zweck(1564)
-
Diskrete Halbleiter-Produkte
Diskrete Halbleiter-Produkte
- Aktuelle Regulierung - Dioden, Transistoren(1090)
- Transistoren-besonderer Zweck(226)
- Transistoren-programmierbare Unijunction(48)
- Transistoren-jfets(1558)
- Transistoren-IGBTs-Einzel(4799)
- Transistoren-IGBTs-Module(63420)
- Transistoren-IGBTs-Arrays(26)
- Transistoren-FETs, MOSFETs-Einzel(48330)
- Transistoren-FETs, MOSFETs-RF(4903)
- Transistoren-FETs, MOSFETs-Arrays(6641)
- Transistoren-Bipolar (BJT)-einzeln, Pre-biased(4539)
- Transistoren-Bipolar (BJT)-Einzel(25800)
- Transistoren-Bipolar (BJT)-RF(2087)
- Transistoren-bipolare (BJT)-Arrays, Pre-biased(2115)
- Transistoren-bipolare (BJT)-Arrays(2310)
- Thyristor-triacs(4044)
- Thyristoren-SCRs-Module(3967)
- Thyristoren-SCRs(5436)
- Thyristoren-diacs, sidacs(319)
- Power Driver Module(1627)
- Dioden-zenerdioden-Einzel(87483)
- Dioden-zenerdioden-Arrays(2619)
- Dioden - variable Kapazität (Varik, Varaktoren)(1200)
- Dioden-RF(2753)
- Dioden-Gleichrichter-Einzel(67528)
- Dioden-Gleichrichter-Arrays(20581)
- Dioden-Brücke-Gleichrichter(11700)
-
RF/if und RFID
RF/if und RFID
- SIM -Karten für Abonnenten -Identifikationsmodul (SIM)(77)
- RF -Zirkulatoren und Isolatoren(1742)
- RFID, RF-Zugang, Monitoring-ICS(1550)
- RFID Transponder, Tags(747)
- RFID Lesegeräte(464)
- RFID -Bewertungs- und Entwicklungskits, Boards(30)
- RFID Antennen(329)
- RFI und EMI - Abschirm- und Absorbungsmaterialien(6444)
- HF und EMI-Kontakte, Fingerstock und Dichtungen(7497)
- RF Transmitter(668)
- RF Transceiver Module(6900)
- RF-Transceiver ICS(4169)
- HF-Schalter(9276)
- RF Shields(16401)
- HF-Receiver(1998)
- HF -Empfänger, Sender und Transceiver -Einheiten(2763)
- RF Power Divider/Splitter(1223)
- RF Power Controller ICs(86)
- HF-Modulatoren(710)
- HF-Mixer(2800)
- RF misc ICS und Module(3276)
- HF-Front-End (LNA + PA)(419)
- RF -Bewertungs- und Entwicklungskits, Boards(747)
- HF-gerichtete Kupplung(2718)
- RF Diplexer(1464)
- RF-Detektoren(412)
- RF-Demodulatoren(249)
- HF-Antennen(12319)
- HF-Verstärker(19651)
- Balun(1496)
- Dämpfungsglieder(4852)
-
Optoelektronik
Optoelektronik
- Optomechanisch(480)
- Leuchten(125)
- Laserdioden, Lasermodule - Laserlieferung, Laserfasern(345)
- Hene Lasersysteme(31)
- Hene Laserköpfe(27)
- Hintergrundbeleuchtung anzeigen(93)
- Xenon-Beleuchtung(387)
- Touchscreen-Overlays(453)
- Panel Indicators, Pilot Lights(75729)
- Optik-Remote-Phosphor-Lichtquelle(269)
- Optik-Reflektoren(665)
- Optik-leichte Rohre(5384)
- Optik-Objektive(4951)
- LEDs-Spacer, Unentschieden(2718)
- LEDs-Lamp-Ersetzungen(29718)
- LEDs - Leiterplattenindikatoren, Arrays, Lichtstäbe, Balkendiagramme(9083)
- LED-thermische Produkte(667)
- LED-Beleuchtung(64)
- LED-Beleuchtung-weiß(37580)
- LED-Beleuchtung-Farbe(4728)
- LED-Beleuchtung-Maiskolben, Motoren, Module(28735)
- LED-Anzeige-diskret(27601)
- Laserdioden, Module(1553)
- Lampen-Glühlampen, Neons(311004)
- Lampen-Kälte-Fluoreszenz (KKL) & UV(164)
- Wechselrichter(7728)
- Infrarot, UV, sichtbare Strahler(3871)
- Fiber Optics-Transmitter-Antrieb integriert(4085)
- Fiber Optics-Transmitter-diskrete(350)
- Fiber Optics-Transceiver Module(18758)
- Fiberoptik-Switches, Multiplexer, Demultiplexer(1387)
- Fiberoptik-Receiver(695)
- Fiberoptik-Dämpfung(654)
- Elektrolumineszenz(102)
- Display, Monitor-Interface Controller(98)
- Display-Module-Vakuum-Leuchtstofflampen (VFD)(249)
- Module anzeigen-LED Dot Matrix und Cluster(865)
- Display-Module-LED-Zeichen und numerische(5421)
- Display-Module-LCD, OLED, Graphic(4654)
- Display-Module-LCD, OLED-Zeichen und numerische(2202)
- Display-Blenden, Objektive(88)
- Adresse, Spezialität(458)
-
Sensoren, Wandler
Sensoren, Wandler
- Ultraschallempfänger, Sender - Industrial(115)
- Temperatursensoren - Thermostate - Mechanisch - Industrielles(3103)
- Temperatursensoren - Analog und digitaler Ausgang - Industrial(209)
- Näherungssensoren - Industrial(13611)
- Drucksensoren, Wandler - Industrie(26503)
- Optische Sensoren - Photonik - Zähler, Detektoren, SPCM (Einzelphotonzählmodul)(751)
- Optische Sensoren - Kameramodule(875)
- Magnetsensoren - Position, Nähe, Geschwindigkeit (Module) - Industrie(554)
- Kraftsensoren - Industrial(346)
- Flusssensoren - Industrielles(151)
- Float, Level Sensoren - Industrial(310)
- Encoder - Industrial(4980)
- Farbsensoren - Industrial(50)
- Berührungssensoren(100)
- Ultraschall-Receiver, Transmitter(2421)
- Temperatursensoren-Thermostat-Solid State(1096)
- Temperatursensoren-Thermostate-mechanisch(3397)
- Temperatursensoren - Thermoelemente, Temperatursonden(1921)
- Temperatursensoren - RTD (Widerstandstemperaturdetektor)(1525)
- Temperatursensoren-PTC-Thermistoren(2273)
- Temperatursensoren-ntc-thermistoren(13259)
- Temperatursensoren-Analog und Digital Output(3928)
- DMS(1399)
- Spezialisierte Sensoren(1861)
- Solarzellen(503)
- Schock-Sensoren(84)
- Sensor-Interface-Junction-Blöcke(2519)
- Sensor-Kabel-Baugruppen(22011)
- Proximity/Belegung Sensoren-fertige Einheiten(725)
- Näherungsschalter(2860)
- Drucksensoren, Wandler(11317)
- Positionssensoren - Winkel, lineare Positionsmessung(6022)
- Optische Sensoren-reflektierende-Logik-Ausgang(194)
- Optische Sensoren - reflektierend - analoge Ausgang(432)
- Optische Sensoren-Phototransistoren(1027)
- Optische Sensoren - Photointerrupter - Schlitztyp - Transistorausgang(1427)
- Optische Sensoren - Photointerrupter - Schlitztyp - Logikausgabe(1215)
- Optische Sensoren-Lichtschranke, Industrial(16763)
- Optische Sensoren-Photodioden(1543)
- Optische Sensoren-Foto-Detektoren-Remote Receiver(2605)
- Optische Sensoren-Foto-Detektoren-Logik-Ausgang(146)
- Optische Sensoren-Foto-Detektoren-CDs-Zellen(74)
- Optische Sensoren-Distanz-Messung(377)
- Optische Sensoren-Ambient Light, IR, UV Sensoren(1305)
- Multifunktions(558)
- Motion Sensors-Vibration(337)
- Motion Sensors-Tilt Schalter(67)
- Bewegungsmelder-optisch(719)
- Motion Sensors-Neigungssensoren(175)
- Motion Sensors-Imus (Trägheit-Maßeinheiten)(416)
- Motion Sensors-Kreisel(214)
- Motion Sensors-Beschleunigungsmesser(1911)
- Magnete-Sensor abgestimmt(119)
- Magnete-Multi Purpose(1965)
- Magnetische Sensoren-Schalter (Solid State)(3700)
- Magnetsensoren - Position, Nähe, Geschwindigkeit (Module)(5199)
- Magnetische Sensoren-linear, Kompass (ICS)(1247)
- Magnetsensoren - Kompass, Magnetfeld (Module)(35)
- LVDT -Wandler (linearer variabler Differentialtransformator)(204)
- IrDA Transceiver-Module(196)
- Bildsensor, Kamera(2235)
- Feuchtigkeit-Sensoren(1425)
- Gas-Sensoren(1217)
- Force Sensoren(188)
- Durchfluss-Sensoren(550)
- Float, Level Sensoren(1343)
- Encoder(6357)
- Staub-Sensoren(43)
- Aktuelle Wandler(3455)
- Color Sensoren(85)
- Verstärker(1905)
-
Anschlüsse, Verbindungen
Anschlüsse, Verbindungen
- USB, DVI, HDMI -Stecker(446)
- Festkörperbeleuchtungsstecker(555)
- Steckdosen für ICs, Transistoren(953)
- Steckbare Steckverbinder(1221)
- Photovoltaik (Solarpanel) Anschlüsse(136)
- Glasfaseranschlüsse(370)
- FFC, FPC (flache flexible) Anschlüsse(761)
- D-Sub, D-förmige Stecker(2887)
- Koaxialverbinder (RF)(2389)
- Rundanschlüsse(14162)
- Stromanbeter Blade Type(273)
- Stecker und Behälter(2597)
- USB, DVI, HDMI Stecker-Adapter(572)
- USB, DVI, HDMI -Stecker(4298)
- Klemmen-Wire to Board Steckverbinder(217)
- Klemmen-Draht-Steckverbinder(4322)
- Klemmen-Draht-Pin Stecker(328)
- Terminals-Revolver Steckverbinder(1273)
- Terminals-spezialisierte Steckverbinder(2042)
- Klemmen-Spaten Verbinder(3902)
- Klemmen-Löten/Stecker(345)
- Klemmen-Verschraubungen(745)
- Klemmen-Ring Steckverbinder(12596)
- Klemmen-rechteckige Steckverbinder(4747)
- Terminals - Schnellverbindungen, schnelle Trennungsanschlüsse(8514)
- Klemmen-PC PIN, Single Post Connectors(3776)
- Klemmen-PC-Pin-Buchsen, Sockel-Steckverbinder(5883)
- Klemmen-magnetische Draht-Steckverbinder(1653)
- Klemmen-Messer Steckverbinder(112)
- Klemmen-Gehäuse, Stiefel(2850)
- Klemmen-Folie Steckverbinder(108)
- Klemmen-Barrel, Bullet-Steckverbinder(1107)
- Klemmen-Adapter(137)
- Terminal-Streifen und Revolver-Boards(1159)
- Terminal Junction Systeme(2533)
- Anschlussblöcke-Draht an Bord(43615)
- Terminal Blocks-spezialisierte(3722)
- Terminal Blocks-Power Distribution(847)
- Anschlussblöcke-Panel Mount(1359)
- Terminal Blocks-Interface Module(1819)
- Anschlussblöcke-Kopfzeilen, Stecker und Buchsen(119920)
- Anschlussblöcke-DIN-Schiene, Kanal(9373)
- Anschlussblöcke-Kontakte(65)
- Anschlussblöcke-Barrier Blocks(47517)
- Anschlussblöcke-Adapter(1059)
- Solid State Lighting Verbinder-Kontakte(271)
- Festkörperbeleuchtungsstecker(1344)
- Buchsen für ICS, Transistoren-Adapter(275)
- Steckdosen für ICs, Transistoren(22148)
- Shunts, Jumper(907)
- Rechteckige Verbinder-Feder geladen(7721)
- Rechteckige Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(43023)
- Rechteckige Verbinder-Kopfzeilen, Spezial-PIN(6129)
- Rechteckige Anschlüsse - Header, Gefäße, weibliche Sockel(229601)
- Rechteckige Verbinder-Kopfzeilen, männliche Pins(543338)
- Rechteckige Anschlüsse - kostenloses Hängen, Panelhalterung(30142)
- Rechteckige Verbinder-Kontakte(10681)
- Rechteckige Anschlüsse - Board in, Direktdraht zum Board(2432)
- Rechteckige Verbinder-Adapter(475)
- Rechteckig - Brett zu Board -Steckern - Header, Behälter, weibliche Sockel(9)
- Rechteckig - Brett zu Board -Steckern - Header, männliche Stifte(2)
- Rechteckige Anschlüsse - Board -Abstandshalter, Stacker (Board zu Board)(238901)
- Rechteckige Anschlüsse - Arrays, Kantentyp, Mezzanin (Board zu Board)(37853)
- Stromanschluss-Eingänge, Steckdosen, Module(10310)
- Steckbare Steckverbinder(6049)
- Photovoltaik- (Solarpanel) Anschlüsse - Kontakte(77)
- Photovoltaik (Solarpanel) Anschlüsse(504)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Verdrahtung Blöcke(99)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Stecker(1674)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Stecker Gehäuse(181)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Buchsen mit magnetischen(10152)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Buchsen(23416)
- Modulare Steckverbinder-Adapter(855)
- Memory Connectors-PC Cards-Adapter(21)
- Memory Connectors-PC Card Sockets(3299)
- Memory Connectors-Inline Modul Sockets(3390)
- LGH Steckverbinder(764)
- Keystone-Einsätze(2758)
- Keystone-Frontplatte, Frames(1926)
- Heavy Duty Steckverbinder-Einsätze, Module(4190)
- Schwerlastanschlüsse - Gehäuse, Kapuzen, Basen(17226)
- Heavy Duty Steckverbinder-Frames(523)
- Heavy Duty Steckverbinder-Kontakte(1832)
- Heavy Duty Steckverbinder-Baugruppen(671)
- LWL-Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(919)
- Glasfaser-Steckverbinder - Adapter(4455)
- LWL-Steckverbinder(3001)
- FFC, FPC (flache flexible) Steckverbinder - Gehäuse(652)
- FFC, FPC (flache flexible) Anschlüsse - Kontakte(202)
- FFC, FPC (flache flexible) Anschlüsse(18691)
- D-Sub, d-förmige Steckverbinder-Terminatoren(47)
- D-Sub, d-förmige Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(12238)
- D-Sub, d-förmige Steckverbinder-Kontakte(2714)
- D-Sub, D-förmige Steckverbinder-Rückenschalen, Kapuzen(5995)
- D-Sub, d-förmige Steckverbinder-Adapter(1304)
- D-Sub Steckverbinder(141346)
- D-förmige Steckverbinder-Centronics(8770)
- Kontakte, Frühling geladen und Druck(630)
- Kontakte-Multi Purpose(6196)
- Kontakte-"Leadframe"(122)
- Koaxial-Steckverbinder (RF)-Terminatoren(1231)
- Koaxial-Steckverbinder (RF)-Kontakte(480)
- Koaxial-Steckverbinder (RF)-Adapter(6386)
- Koaxialverbinder (RF)(25734)
- Rundsteckverbinder-Gehäuse(441226)
- Rundsteckverbinder-Kontakte(4737)
- Rundsteckverbinder-backschalen und Kabel-Klemmen(53692)
- Rundsteckverbinder-Adapter(8839)
- Rundanschlüsse(1196254)
- Card Edge Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(469)
- Karte Edge Verbinder-edgeboard Verbinder(672683)
- Card Edge Verbinder-Kontakte(325)
- Card Edge Verbinder-Adapter(73)
- Blade Type Power Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(837)
- Blade Type Power Connectors-Kontakte(393)
- Stromanbeter Blade Type(4163)
- Zwischen Serien-Adapter(649)
- Barrel-Stromanschluss(935)
- Barrel-Audio-Anschlüsse(2432)
- Barrel-Audio Adapter(92)
- Banana und Tip Steckverbinder-Buchsen, Stecker(1644)
- Banana and Tip Connectors-Binding Posts(239)
- Banana und Tip Steckverbinder-Adapter(75)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-spezialisiert(45586)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-Gehäuse(6863)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-Hard metrisch, Standard(6297)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-DIN 41612(9408)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-Kontakte(3583)
- Backplane Connectors-ARINC Einsätze(2357)
- Backplane Steckverbinder-ARINC(3789)
-
Widerstände
-
Kondensatoren
Kondensatoren
- Aluminium-Elektrolytkondensatoren(16817)
- Trimmer, Variable Kondensatoren(3151)
- Dünne Folien-Kondensatoren(3473)
- Tantal-Kondensatoren(136103)
- Tantal-Polymer-Kondensatoren(9778)
- Silizium-Kondensatoren(320)
- Niob Oxide Kondensatoren(330)
- Mica und PTFE Kondensatoren(9101)
- Folien-Kondensatoren(150406)
- Elektrische Doppelschichtkondensatoren (EDLC), Superkondensatoren(2782)
- Keramische Kondensatoren(833829)
- Kondensatoren-Netzwerke, Arrays(2383)
- Aluminium-Elektrolytkondensatoren(125325)
- Aluminium-Polymer-Kondensatoren(7544)
-
Transformatoren
-
Isolatoren
-
Kristalle, Oszillatoren, Resonatoren
-
Switches
Switches
- Verriegelungsschalter(2893)
- Emergency-Stop-Schalter (E-Stop)(1160)
- Kabelzugschalter(571)
- Toggle-Schalter(33608)
- Rändelrads Schalter(742)
- Schalter(14263)
- Snap-Aktion, Endschalter begrenzen(28077)
- Slide-Schalter(5166)
- Selector-Schalter(9720)
- Rotary Switches(13850)
- Rocker Schalter(53790)
- Drucktaste-Schalter-Hall-Effekt(127)
- Drucktaste Schalter(190826)
- Programmierbare Display-Switches(39)
- Navigations-Schalter, Joystick(1882)
- Magnetische, Reed-Schalter(1399)
- Keypad-Schalter(637)
- Keylock Schalter(3684)
- DIP Schalter(7747)
- Konfigurierbare Switch-Komponenten-Objektiv(1435)
- Konfigurierbare Schalter-Komponenten-Lichtquelle(1236)
- Konfigurierbare Switch-Komponenten-Contact Block(1401)
- Konfigurierbare Switch-Komponenten-Body(16077)
- Disconnect-Switch-Komponenten(2567)
-
Relais
Relais
- Sicherheitsrelais(1310)
- Reedrelais(1735)
- Hochfrequenz (RF) -Relais(1190)
- Schütze (Festkörper)(686)
- Schütze (elektromechanisch)(11952)
- Kfz-Relais(1881)
- Solid State Relais(10652)
- Signal-Relais, bis zu 2 Ampere(9149)
- Relay-Sockets(2075)
- Power Relays, über 2 Ampere(31604)
- E / A-Relaismodule(712)
- I/o-Relay-Module-Input(2)
- I/o-Relay-Modul-Racks(247)
Sprache auswählen
Aktuelle Sprache
Deutsch
- English
- Deutsch
- Italia
- Français
- 日本語
- 한국의
- русский
- Svenska
- Nederland
- español
- Português
- polski
- Suomi
- Gaeilge
- Slovenská
- Slovenija
- Čeština
- Melayu
- Magyarország
- Hrvatska
- Dansk
- românesc
- Indonesia
- Ελλάδα
- Български език
- Afrikaans
- IsiXhosa
- isiZulu
- lietuvių
- Maori
- Kongeriket
- Монголулс
- O'zbek
- Tiếng Việt
- हिंदी
- اردو
- Kurdî
- Català
- Bosna
- Euskera
- العربية
- فارسی
- Corsa
- Chicheŵa
- עִבְרִית
- Latviešu
- Hausa
- Беларусь
- አማርኛ
- Republika e Shqipërisë
- Eesti Vabariik
- íslenska
- မြန်မာ
- Македонски
- Lëtzebuergesch
- საქართველო
- Cambodia
- Pilipino
- Azərbaycan
- ພາສາລາວ
- বাংলা ভাষার
- پښتو
- malaɡasʲ
- Кыргыз тили
- Ayiti
- Қазақша
- Samoa
- සිංහල
- ภาษาไทย
- Україна
- Kiswahili
- Cрпски
- Galego
- नेपाली
- Sesotho
- Тоҷикӣ
- Türk dili
- ગુજરાતી
- ಕನ್ನಡkannaḍa
- मराठी
Flyback -Transformatoren verstehen
Zeit: 2024/10/25
Durchsuchen: 2,179
Katalog
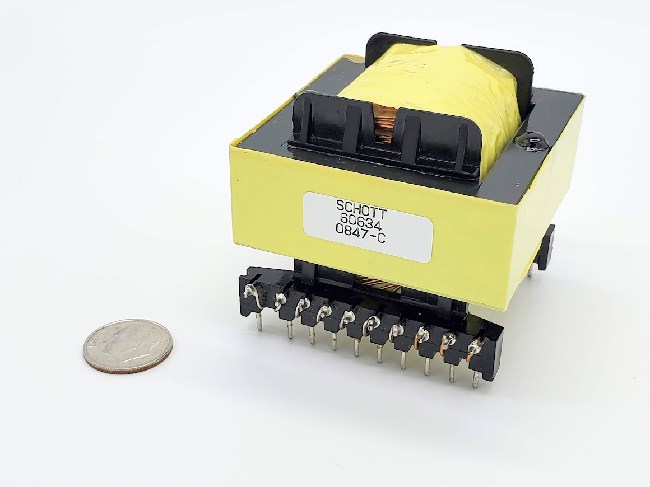
Eigenschaften von Flyback -Transformatoren
Ein Flyback -Transformator ist ein kleines, effizientes Gerät, das die Spannung effizient erhöhen kann und häufig bei CRT -Fernsehern und Stromversorgungssystemen verwendet wird.Im Gegensatz zu regulären Transformatoren, die Wechselstrom (AC) verwenden, arbeiten Flyback -Transformatoren mit Gleichstromimpulsen (DC).Zum Beispiel können sie einen Eingang von 230 V aufnehmen und ihn auf bis zu 20.000 V erhöhen.Sie können auch mit niedrigeren DC -Eingängen wie 5 V oder 12 V arbeiten.Obwohl ihre Hochspannungsausgabe nicht zum Versenden von Strom über große Strecken nicht geeignet ist, eignet sie sich perfekt für spezifische Verwendungen, z.
Flyback -Transformatoren haben ein einzigartiges Design mit zwei Wicklungen, die als Primär- und Sekundärwicklungen bezeichnet werden und bei denen die sekundäre Wicklung normalerweise dicker ist, um die Spannungsausgabe zu erhöhen.Kondensatoren tragen dazu bei, die Spannung stabil zu halten, und die Dioden steuern die Richtung des Stroms und sorgen für einen stabilen Ausgang.Die "Punktkonvention" des Transformators zeigt, wie diese Wicklungen zusammenarbeiten, um die Effizienz zu verbessern.
Diese Transformatoren können Hochspannungen von 10 bis 20 kV erzeugen, was manchmal zu elektrischen Bögen führt, wenn leitende Materialien in der Nähe sind.Die sekundäre Wicklung besteht aus Kupfer und isoliert mit Materialien wie Glimmer, wodurch der Transformator effizienter und umweltfreundlicher wird, indem der Ölverbrauch vermieden wird.Dieses Design senkt die Energieverluste und verringert die Wartung.
Flyback -Transformatoren sind für moderne Geräte praktisch, da sie effizient mit niedrigen Stromeingängen zusammenarbeiten, kompakt sind und weniger Wartung erfordern, was sie zu einer guten Option macht, wo Raum und Nachhaltigkeitsmaterial wichtig sind.
Betrieb und Funktionalität
Der Betrieb eines Flyback -Transformators ähnelt den regulären Transformatoren, aber mit einigen Unterschieden, die es für bestimmte Verwendungszwecke effizienter machen.Ein niedriger Spannungsstrom, der als Sägezahnwellenform bezeichnet wird, wird in die primäre Wicklung gesendet.Wenn der Strom steigt, baut sie Energie auf, bis es einen Höhepunkt erreicht.Dioden werden in die Schaltung gestellt, um zu verhindern, dass der Strom nach hinten fließt und sicherstellt, dass sich der Strom in eine Richtung bewegt.Wenn der Strom in der sekundären Wicklung zu sinken beginnt, wird eine Hochspannung erzeugt, wodurch der elektrische Strom in eine Richtung führt.Mit diesem Vorgang kann der Flyback -Transformator effizient funktionieren und den Wechselstrom (AC) in geschaltete Modi umwandeln, bei denen die Stromversorgung nach Bedarf ein- und ausgeschaltet werden kann.
Flyback -Transformers bestehen aus zwei Wicklungen - primär und sekundär - um einen magnetischen Kern geworfen.Die Primärwicklung hat normalerweise weniger Kurven als die Sekundär, sodass der Transformator die Spannung steigern kann.Kupfer wird in den Wicklungen verwendet, da es ein guter Leiter ist und eine starke Isolierung bietet.Der magnetische Kern eignet sich hervorragend für die Fähigkeit des Transformators, Hochspannungen selbst mit niedriger Leistung zu bewältigen.Das Design dieses Kerns spielt eine Rolle bei der effizienten und zuverlässigsten Funktionsweise des Transformators.Diese sorgfältige Balance zwischen dem Kerndesign und der Wickelanordnung macht Flyback -Transformatoren zu einer Hauptkomponente in vielen fortschrittlichen elektronischen Systemen wie Netzteilen und Fernsehern.
Anwendungen von Flyback -Transformatoren
Flyback -Transformatoren werden in vielen großartigen Bereichen wie alten Fernsehbildschirmen (CRT -Röhren), Netzteilen (SMPs), Batterieladeern, Telekommunikations- und Solarenergiesystemen verwendet.Ihre geringe Größe und Fähigkeit, Hochspannung zu erzeugen, machen sie in verschiedenen Feldern nützlich.Aber wie helfen sie heute die Technologie?Ihre Fähigkeit, sich an verschiedene Bedürfnisse anzupassen, macht sie so wertvoll.
CRT -Röhrchen
In der Vergangenheit wurden Flyback -Transformatoren in alten Fernsehbildschirmen mit CRT -Röhren verwendet, um die für Bilder benötigte Hochspannung zu erzeugen.Heute verwenden wir LCD- und OLED -Bildschirme, aber Flyback -Transformatoren zeigen immer noch, wie ältere Technologien neuere dazu beigetragen haben, zu wachsen.Ideen von diesen Transformatoren helfen zukünftige Tariftechnologien.Sie haben sicherlich eine große Rolle in früheren Innovationen gespielt.
Netzteile ausgeschaltetem Modus (SMPS)
Flyback-Transformatoren sind in SMPS-Netzteilen (Switched-Mode Netzteil) erforderlich, wo sie dazu beitragen, die Spannung mit sehr geringem Energieverlust zu ändern.Dies ist in vielen Geräten wie Laptops und Fernseher nützlich.Da sie klein und leicht sind, helfen sie auch dabei, die Energieelektronik kleiner zu machen.Was macht diese Transformatoren so effizient?Es ist ihr besonderes Design und die Materialien, die sie bauen.
DC-DC-Konvertierung
Flyback-Transformatoren sind in der DC-DC-Leistungsumwandlung ein Hauptverkehr, was bedeutet, dass sie dazu beitragen, die DC-Spannung (Gleichstroms (DC) auf eine andere Ebene zu ändern.Dies ist nützlich bei Autos und tragbaren Elektronik, wo Platz und Effizienz von Bedeutung sind.Helfen sie bei Elektroautos?Ja, weil ihre Flexibilität in der wachsenden Elektrofahrzeugindustrie sehr hilfreich ist.
Batterieladesysteme
In Batterieladeern helfen Flyback -Transformatoren, die Spannung und den Strom zu steuern und sicherzustellen, dass die Batterien sicher und effizient laden.Bei dem Design geht es darum, das richtige Gleichgewicht zwischen Leistung und Sicherheit zu finden.Gibt es irgendwelche Kompromisse?Manchmal kann die Auswahl eines sichereren Designs die Leistung leicht verringern, aber die Sicherheit hat Priorität.
Telekommunikation
In Telekommunikation werden Flyback -Transformatoren in Stromversorgungen für Netzwerkgeräte verwendet, wodurch die Systeme stabil und zuverlässig bleiben.Dies ist für eine reibungslose Kommunikation sehr erforderlich.Wie hilft dies für die Netzwerksicherheit?Durch die Bereitstellung einer stabilen Leistung verringern sie das Risiko von Störungen, was die Sicherheit und Zuverlässigkeit des Netzwerks erhöht.
Solarenergiesysteme
In Solarenergiesystemen sind Flyback -Transformatoren Teil von Wechselrichterschaltungen, die DC von Sonnenkollektoren in Wechselstrom wechseln, die wir für Elektrizität verwenden.Dies ist grundlegend für die Verbindung von Solarenergie mit dem Stromnetz und hilft uns, umweltfreundlichere Lösungen zu bewegt.Die Verwaltung von Wärme und Verbesserung der verwendeten Materialien sind immer noch große Herausforderungen.
Häufig gestellte Fragen [FAQ]
1. Wie testet man einen Flyback -Transformator?
Sie können einen Flyback -Transformator mit mehreren Methoden testen.Ein linienbetriebener potenzieller Transformator-Tester wird üblicherweise verwendet, um Wickelfehler durch Messung der Impedanz zu erkennen.Wenn die Wicklung offen ist, zeigt der Tester eine sehr hohe Impedanz;Wenn es einen Kurzschluss gibt, liest die Impedanz niedrig.Viele moderne Tester bieten auch ein grafisches Display an, um die Gesundheit zu zeigen.
Bei Kondensatorproblemen hören Sie auf ein "TIC-TAC" -Reary, das auf einen offenen Kondensator hinweist.Eine kurze Leistung auf dem Display signalisiert normalerweise einen verkürzten Kondensator, was bedeutet, dass der Kondensator wahrscheinlich ersetzt werden muss.Andere häufige Probleme, wie Kurzwinde, Kernrisse oder externes Lichtbogen, können ebenfalls mit einem zeilenbetriebenen Tester überprüft werden.Zusätzlich kann ein Standard -Multimeter dazu beitragen, die Kontinuität der Schaltung zu bestätigen und die Spannung an jedem Punkt zu messen, wodurch überprüft wird, ob alle Komponenten korrekt funktionieren.
2. Was macht ein Flyback -Transformator?
Ein Flyback -Transformator ist ein gekoppelter Induktor mit einem Gitterkern.Wenn die primäre Wicklung Eingangsspannung erhält, speichert sie Energie in jedem Zyklus in der Lücke des Kerns.Diese Transformatoren werden in Flyback -Wandlern verwendet, um Spannungsumwandlung und Schaltungsisolierung bereitzustellen.
3. Wie viele Volt erzeugt ein Flyback -Transformator?
Flyback -Transformatoren oder Leitungsausgangstransformatoren haben ein einzigartiges Design mit gekoppelten Induktoren.Sie können aus wenigen Kilovolten bis zu 50 Kilovolt erzeugen und bei hohen Frequenzen arbeiten, typischerweise zwischen 17 kHz und 50 kHz.
4. Woher weiß ich, ob mein Flyback -Transformator schlecht ist?
Ein fehlerhafter Flyback -Transformator führt häufig dazu, dass der Monitor seine Bildanzeige verliert, auch wenn der Ton weiter spielt.Dies geschieht, weil der Transformator nicht genügend Hochspannung liefert, um ein sichtbares Bild zu erzeugen.Ohne diese Spannung bleibt der Monitor aktiv, kann aber keine visuelle Ausgabe anzeigen.
Verwandter Artikel
-
Oct 25 2024Ladung von Trolling -Motorbatterien mit Sonnenkollektoren
Angesichts der steigenden Beliebtheit nachhaltiger Energie und der Fortschritte bei der Solartechnologie sind viele Bootsfahrer neugierig, ob sie Sola... -
Oct 25 2024Berechnung der Solarpanelwattage
Das Verständnis von Solarpanelberechnungen kann für Sie verwirrend sein.Es geht nicht nur darum, die Panel zu überprüfen.Es beinhaltet viele Fakto...
Verwandte -Produkte

T350B155K035AS
CAP TANT 1.5UF 10% 35V RADIAL

L32P100S05FS
SENSOR CURRENT HALL 100A AC/DC

SN74FB2033ARCRG3
IC REGISTERED TXRX 8BIT 52QFP

MB89F053PF-GE1
MB89F053PF-GE1 FUJ

GE28F320C3BC70
GE28F320C3BC70 INTEL
KPC5603PF1VLL6
FREESCALE QFP

LTM2887Y-3S
LTM2887Y-3S LINEAR

STM8AF6168TC
STM8AF6168TC ST

VT1145SCX
IC INTERFACE CONTROLLER

CPICS01192A
PARROT BGA

STLC574DTR
ST TQFP64

MT41K256M16HA-125-E
Relevanzprodukte

C1206X475K3RACTU
CAP CER 4.7UF 25V X7R 1206
vorrätig: 1371